Filter Detections
The advanced filtering capabilities of the Detections class offer users a versatile and efficient way to narrow down
and refine object detections. This section outlines various filtering methods, including filtering by specific class
or a set of classes, confidence, object area, bounding box area, relative area, box dimensions, and designated zones.
Each method is demonstrated with concise code examples to provide users with a clear understanding of how to implement
the filters in their applications.
by specific class¶
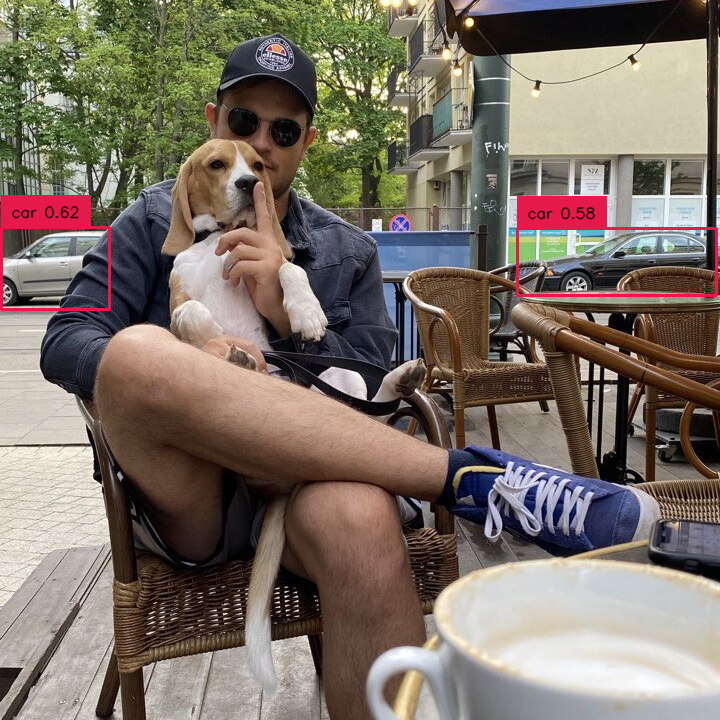
Allows you to select detections that belong only to one selected class.
import supervision as sv
detections = sv.Detections(...)
detections = detections[detections.class_id == 0]

import supervision as sv
detections = sv.Detections(...)
detections = detections[detections.class_id == 0]
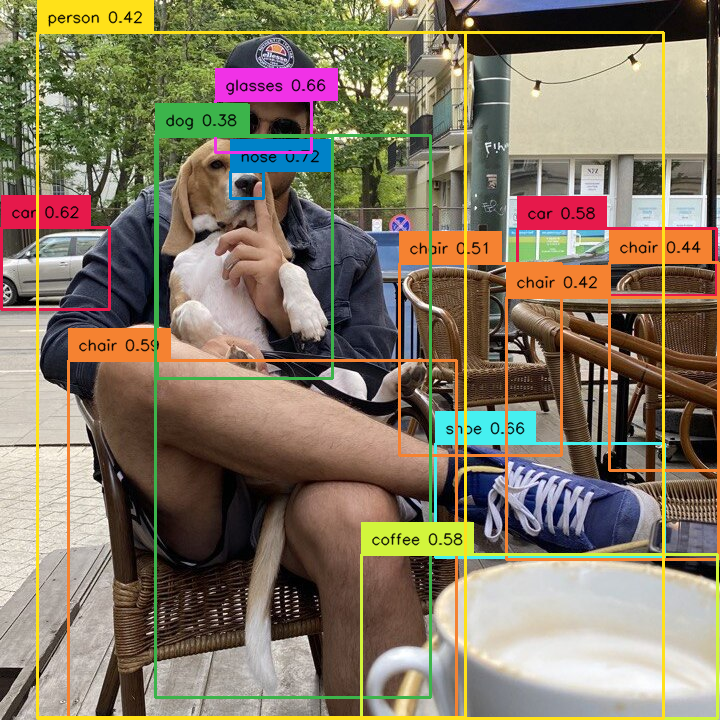
by set of classes¶
Allows you to select detections that belong only to selected set of classes.
import numpy as np
import supervision as sv
selected_classes = [0, 2, 3]
detections = sv.Detections(...)
detections = detections[np.isin(detections.class_id, selected_classes)]

import numpy as np
import supervision as sv
class_id = [0, 2, 3]
detections = sv.Detections(...)
detections = detections[np.isin(detections.class_id, class_id)]

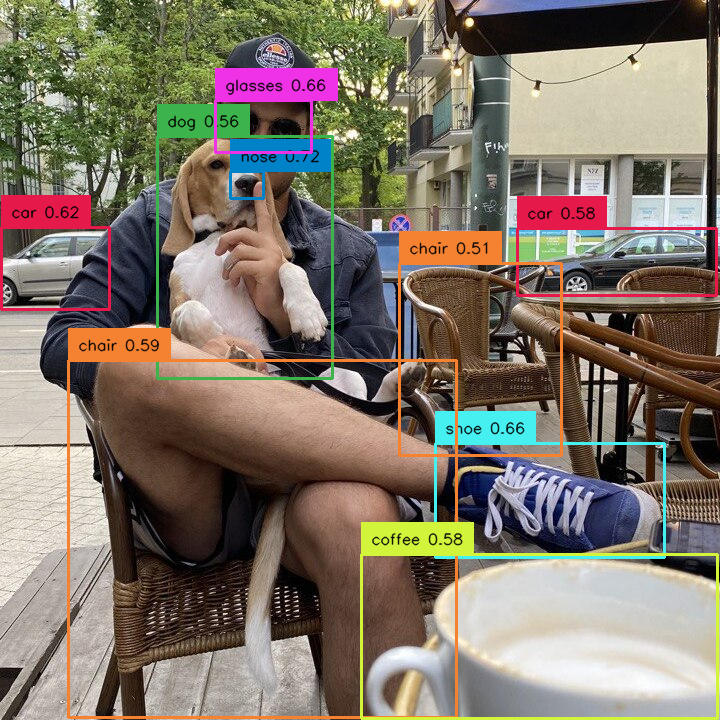
by confidence¶
Allows you to select detections with specific confidence value, for example higher than selected threshold.
import supervision as sv
detections = sv.Detections(...)
detections = detections[detections.confidence > 0.5]
import supervision as sv
detections = sv.Detections(...)
detections = detections[detections.confidence > 0.5]

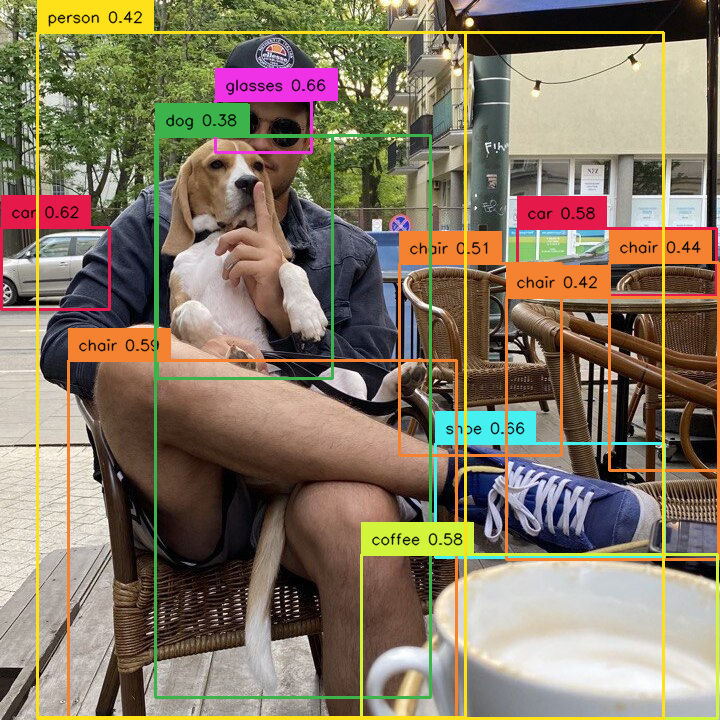
by area¶
Allows you to select detections based on their size. We define the area as the number of pixels occupied by the detection in the image. In the example below, we have sifted out the detections that are too small.
import supervision as sv
detections = sv.Detections(...)
detections = detections[detections.area > 1000]
import supervision as sv
detections = sv.Detections(...)
detections = detections[detections.area > 1000]

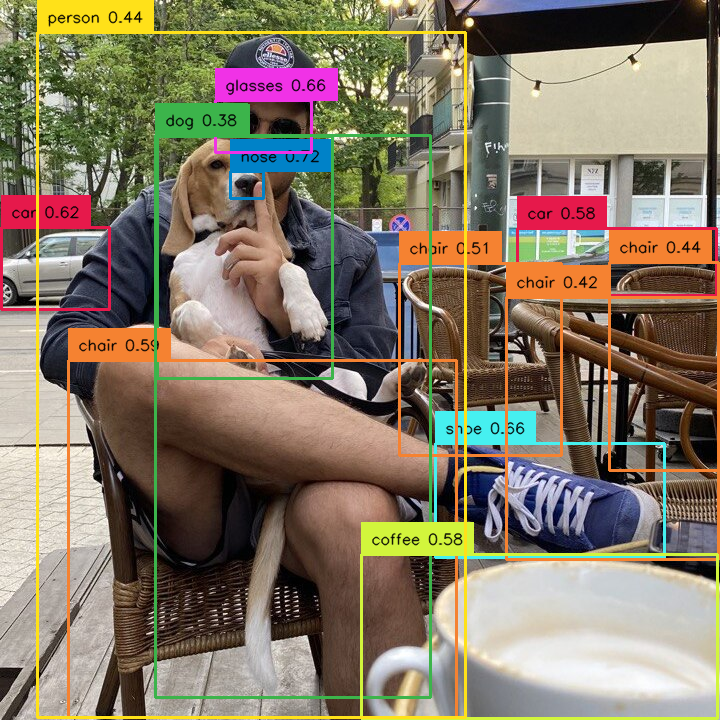
by relative area¶
Allows you to select detections based on their size in relation to the size of whole image. Sometimes the concept of detection size changes depending on the image. Detection occupying 10000 square px can be large on a 1280x720 image but small on a 3840x2160 image. In such cases, we can filter out detections based on the percentage of the image area occupied by them. In the example below, we remove too large detections.
import supervision as sv
image = ...
height, width, channels = image.shape
image_area = height * width
detections = sv.Detections(...)
detections = detections[(detections.area / image_area) < 0.8]
import supervision as sv
image = ...
height, width, channels = image.shape
image_area = height * width
detections = sv.Detections(...)
detections = detections[(detections.area / image_area) < 0.8]

by box dimensions¶
Allows you to select detections based on their dimensions. The size of the bounding box, as well as its coordinates, can be criteria for rejecting detection. Implementing such filtering requires a bit of custom code but is relatively simple and fast.
import supervision as sv
detections = sv.Detections(...)
w = detections.xyxy[:, 2] - detections.xyxy[:, 0]
h = detections.xyxy[:, 3] - detections.xyxy[:, 1]
detections = detections[(w > 200) & (h > 200)]

import supervision as sv
detections = sv.Detections(...)
w = detections.xyxy[:, 2] - detections.xyxy[:, 0]
h = detections.xyxy[:, 3] - detections.xyxy[:, 1]
detections = detections[(w > 200) & (h > 200)]

by PolygonZone¶
Allows you to use Detections in combination with PolygonZone to weed out bounding boxes that are in and out of the
zone. In the example below you can see how to filter out all detections located in the lower part of the image.
import supervision as sv
zone = sv.PolygonZone(...)
detections = sv.Detections(...)
mask = zone.trigger(detections=detections)
detections = detections[mask]

import supervision as sv
zone = sv.PolygonZone(...)
detections = sv.Detections(...)
mask = zone.trigger(detections=detections)
detections = detections[mask]

by mixed conditions¶
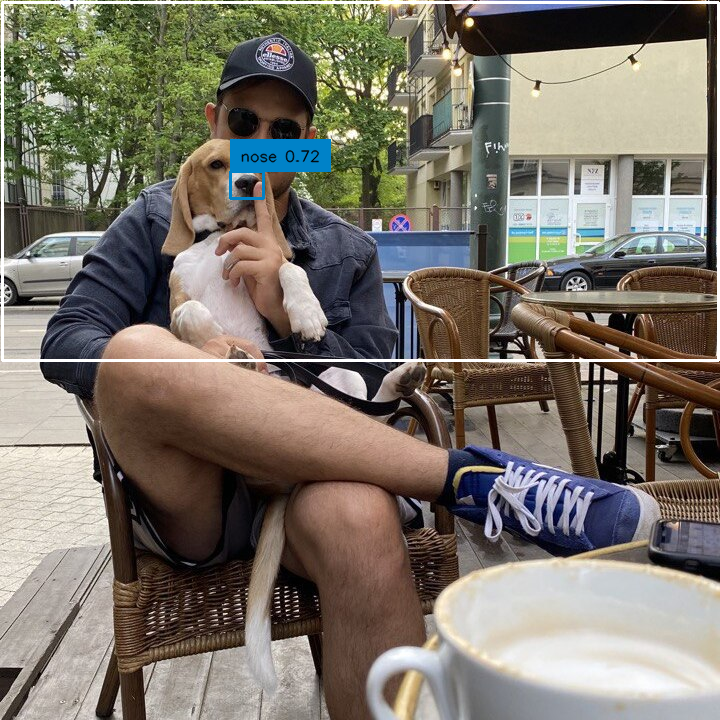
Detections' greatest strength, however, is that you can build arbitrarily complex logical conditions by simply combining separate conditions using & or |.
import supervision as sv
zone = sv.PolygonZone(...)
detections = sv.Detections(...)
mask = zone.trigger(detections=detections)
detections = detections[(detections.confidence > 0.7) & mask]

import supervision as sv
zone = sv.PolygonZone(...)
detections = sv.Detections(...)
mask = zone.trigger(detections=detections)
detections = detections[mask]
